
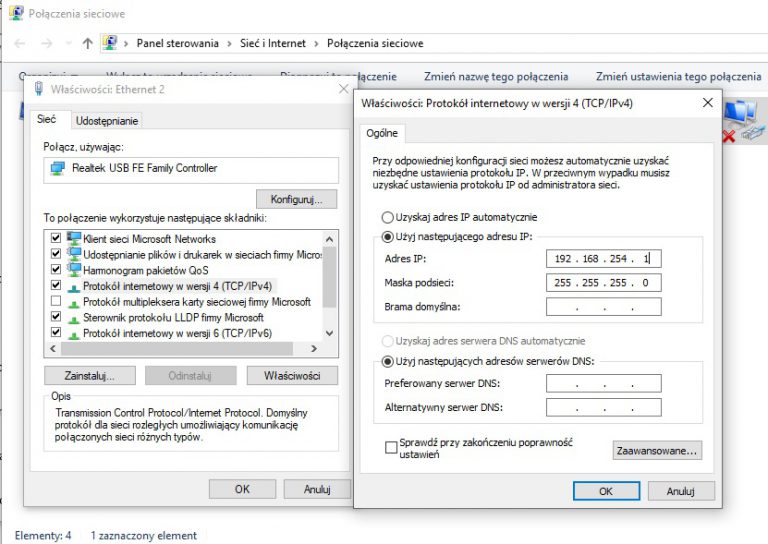
Testing and production į/A-18F Super Hornet (left) and a F/A-18A Hornet (right) As a cheaper alternative to NATF, Grumman proposed substantial improvements to the F-14 beyond Quick Strike, but Congress rejected them as too costly and reaffirmed its commitment to the less expensive F/A-18E/F. In 1992, the Navy canceled the Navy Advanced Tactical Fighter (NATF), which would have been a navalized variant of the Air Force's Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor. The decision to replace the Tomcat with an all-Hornet Carrier Air Wing was controversial Vietnam War ace and Congressman Duke Cunningham criticized the Super Hornet as an unproven design that compromised air superiority. Then-Secretary of Defense Dick Cheney described the F-14 as 1960s technology, and drastically cut back F-14D procurement in 1989 before cancelling production altogether in 1991, in favor of the updated F/A-18E/F. Īt the time, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat was the Navy's primary air superiority fighter and fleet defense interceptor.
#Horner apg upgrade
The next-generation Hornet design proved more attractive than Grumman's Quick Strike upgrade to the F-14 Tomcat, which was regarded as an insufficient technological leap over existing F-14s. In addition, the Hornet itself lacked sufficient bringback capability, or the ability to recover unused weapons aboard aircraft carriers. As an alternative to the A-12, McDonnell Douglas proposed the "Super Hornet" (initially " Hornet II" in the 1980s), an improvement of the successful previous F/A-18 models, which could serve as an alternate replacement for the A-6 Intruder. The Navy considered updating an existing design as a more attractive approach to a clean-sheet program. The McDonnell Douglas A-12 Avenger II was canceled in 1991 after the program ran into serious problems it was intended to replace the obsolete Grumman A-6 Intruder. Naval Aviation faced a number of problems. The end of the Cold War led to a period of military budget cuts and considerable restructuring. The Hornet 2000 concept was an advanced F/A-18 with a larger wing and a longer fuselage to carry more fuel and more powerful engines. The concept of an enlarged Hornet was first proposed in the 1980s, which was marketed by McDonnell Douglas as Hornet 2000. The Hornet proved to be effective but limited in combat radius. The Navy directed that the YF-17 be redesigned into the larger F/A-18 Hornet to meet a requirement for a multi-role fighter to complement the larger and more expensive Grumman F-14 Tomcat serving in fleet defense interceptor and air superiority roles. Later flying as the Northrop YF-17 "Cobra", it competed in the United States Air Force's Lightweight Fighter (LWF) program to produce a smaller and simpler fighter to complement the larger McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle the YF-17 lost the competition to the YF-16. 1965, which began as a rework of the lightweight Northrop F-5E (with a larger wing, twin tail fins and a distinctive leading edge root extension, or LERX). The wing and tail configuration trace its origin to a Northrop prototype aircraft, the P-530, c. The Super Hornet is a redesign of the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet. In February 2023, Boeing announced plans to end production of the Super Hornet in 2025. RAAF Super Hornets entered service in December 2010. The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), which has operated the F/A-18A as its main fighter since 1984, ordered the F/A-18F in 2007 to replace its aging General Dynamics F-111C fleet. The Super Hornet entered fleet service with the United States Navy in 1999, replacing the Grumman F-14 Tomcat, which was retired in 2006 the Super Hornet has served alongside the original Hornet. Low-rate production began in early 1997 with full-rate production starting in September 1997, after the merger of McDonnell Douglas and Boeing the previous month. Additional fuel can be carried in up to five external fuel tanks and the aircraft can be configured as an airborne tanker by adding an external air-to-air refueling system.ĭesigned and initially produced by McDonnell Douglas, the Super Hornet first flew in 1995. The Super Hornet has an internal 20mm M61A2 rotary cannon and can carry air-to-air missiles, air-to-surface and a variety of other weapons. The F/A-18E single-seat and F/A-18F tandem-seat variants are larger and more advanced versions of the F/A-18C and D Hornet. The Boeing F/A-18E and F/A-18F Super Hornet are twin-engine, carrier-capable, multirole fighter aircraft variants derived from the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet series. Boeing Defense, Space & Security (1997–present)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
